December 18, 2025
New Delhi -The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) conducts frequent and organized visual inspections to verify that national highways across the country are safe, durable, and meet required criteria. These inspections are the foundation of highway monitoring, assisting authorities in identifying concerns early, improving safety measures, and ensuring responsibility at all levels of execution.
“Visual inspections play a critical role in identifying risks early and ensuring safer roads for millions of daily commuters.”

Following is a detailed look at the primary components of NHAI’s visual inspection framework:
Purpose of Visual Inspections
Visual inspections are conducted to identify visible deficiencies and risks that can impact road safety and long-term performance. By physically observing highway stretches, officials are able to detect early signs of damage, safety gaps, and non-compliance that may not be evident through reports alone. This proactive approach helps prevent minor issues from turning into major failures.
Key focus areas include:
- detection of cracks, potholes, surface distress, and pavement deformation
- Identifying illumination gaps and poor visibility zones.
- Recognizing unlawful buildings or encroachments
- Assessment of ride quality and user safety
Inspection Frequency and Administrative Oversight
NHAI adheres to a set inspection schedule to ensure ongoing monitoring across areas and projects. To establish checks and balances, officers at different levels are assigned distinct responsibilities. This multilayer inspection approach ensures that no stretch goes undetected for too long.
Inspection responsibilities include:
- Regional officers conduct inspections once every three months.
- Project Directors inspect project stretches monthly.
- Senior officials conduct surprise or special inspections for important passageways.
- Joint inspections of large, complex, or high-risk projects.
On-Ground Inspection Practices
Physical site inspections remain an important feature of the NHAI’s inspection process. These visits enable officials to analyze real-world situations, interact with project teams, and make fast decisions as needed. Night inspections are especially crucial for assessing safety features that are only visible after dark.
On-ground practices involve:
- Daytime and nighttime site inspections for accurate assessment
- Checks in foggy and accident-prone locations.
- Inspection of bridges, flyovers, tunnels, and intersections
- Direct contact with contractors and concessionaires.
Use of Advanced Technology in Inspections
To improve accuracy and efficiency, NHAI augments manual examinations with contemporary technologies. Automated data collecting systems enable the capture of detailed information over lengthy roadway sections in less time, decreasing human error and boosting analytical performance.
Technology tools used include:
- NSVs equipped with 3D laser scanners.
- High-resolution cameras and 360-degree video
- Drones used for aerial assessment of huge or inaccessible places
- Geo-tagged site verification via mobile applications
Digital Documentation and Real-Time Monitoring
All inspection findings are digitally recorded to maintain transparency and accountability. By uploading geo-tagged photographs, videos, and inspection notes to specified portals, NHAI enables real-time defect and corrective action tracking across regions.
Documentation features include:
- Uploading geo-tagged visual evidence
- Centralised dashboards for senior-level monitoring
- The digital mapping of faults and safety gaps
- Time-bound monitoring of rectification status
Construction Quality and Project Monitoring
During the building phase, visual inspections help ensure that work is carried out in accordance with authorized designs and quality standards. Regular monitoring decreases the danger of structural concerns and delays, while pre-commissioning checks guarantee that the facility is ready before it opens to traffic.
Construction-related inspections include:
- Construction-related inspections include:
- Verification of Drawings and Technical Specifications
- Monitoring the construction progress and workmanship.
- Identify design or execution bottlenecks.
- Load testing and safety checks prior to commissioning
Maintenance and Road Safety Evaluation
Inspections of operational roadways are heavily focused on maintenance and safety improvements. Officials inspect road furniture, signage, and safety measures to verify they are functioning and visible under all conditions.
Safety evaluation covers:
- The state of crash barriers, guardrails, and medians
- The placement and clarity of road signs and markers
- Identifying accident blackspots
- Measures to manage fog and improve visibility.
Encroaching and Right-of-Way protection
Encroaching on highways poses major safety and capacity problems. Visual inspections aid in the detection of unauthorized buildings and activities that disrupt traffic flow or jeopardize safety.
Encroachment tests entail:
- Identification of unlawful buildings and entry points
- Violations are documented with photographic proof.
- submission of reports for enforcement action
- Highway land is protected for future expansion.
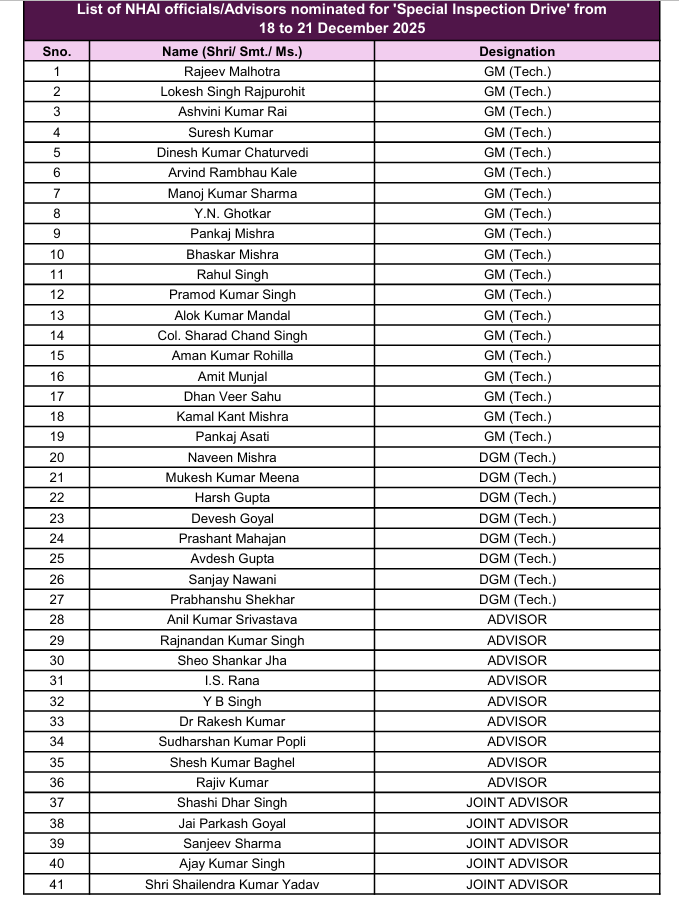
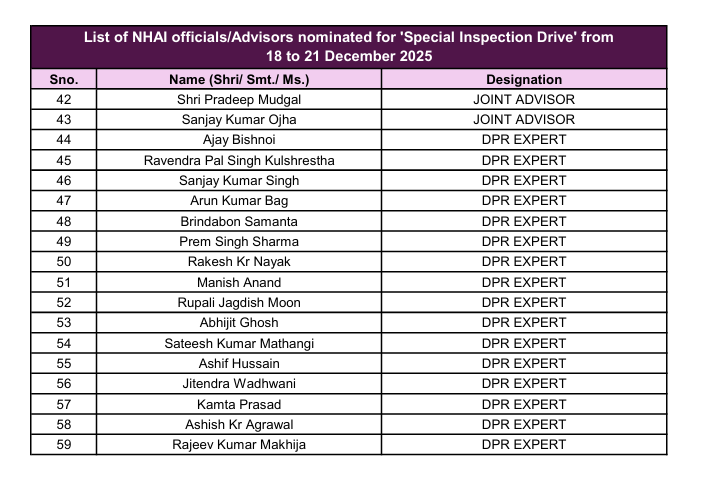
Special Inspection Drives and Targeted Monitoring
The NHAI occasionally organizes special inspection drives to address seasonal obstacles, safety concerns, or region-specific issues. These campaigns involve nominated officials and technical experts who increase monitoring over a set period of time.
Special drives strive to:
- Detect faults and safety issues quickly.
- Enhance accountability via senior-level involvement.
- Take prompt corrective action on key stretches.
- Improve collaboration among field crews.
Coordination, follow-up, and impact
Visual inspections also enable real-time communication among NHAI officials, contractors, and local governments. On-the-spot choices help speed up repairs and improve compliance, resulting in safer and better-maintained highways for motorists.
The key consequences are:
- faster repair of defects
- Increased contractor accountability.
- Better road safety for commuters
- Long-term enhancements in roadway performance
Conclusion
By combining regular field inspections, modern technology, digital monitoring, and special inspection drives, NHAI ensures that National Highways meet high standards of safety and quality. This comprehensive inspection framework reflects a proactive approach to infrastructure management and public safety.
“Strong infrastructure is built not just by construction, but by continuous inspection and accountability.”
The image highlights the nominated officials and advisors assigned for the special inspection drive scheduled from December 18 to December 21, aimed at enhancing on-ground supervision and timely resolution of identified issues.
For more content and updates, visit our YouTube channel:
InfraTalks
Visit our HOMEPAGE for more such articles
